What is Mass in Physics
The greater the mass of a body the smaller the change produced by an applied force. X-Ray Mass Attenuation Coefficients Table 2.

Centre Of Mass Stability Skeletal System Worksheet Physics Wholeness
Questions in paper 2 may draw on an understanding of energy changes and transfers due to heating mechanical and electrical work and the concept of energy conservation from Energy and Electricity.

. Therefore the quantity of mass is conserved over time. Within a given problem domain the amount of mass always should remain constant. It is the exact center of all the material an object is made of.
In this Lesson the motion of a mass on a spring is discussed in detail as we focus on how a variety of quantities change over the course of time. For example you can easily find the center of mass of a ruler. Such quantities will include forces position velocity and energy - both kinetic and potential energy.
Mass is a measure of how much matter there is in an object while weight is a measure of the size of the pull of gravity on the object. Pre-K - 8th grade. 17 Oxford Street Cambridge MA 02138 617 495-2872 phone 617 495-0416 fax.
What is a center of mass. Mass in physics quantitative measure of inertia a fundamental property of all matter. Mass is the amount of.
Every object has a center of mass. The motion of a mass attached to a spring is an example of a vibrating system. Try holding your.
The mass of any object is simply the volume that is occupied by the object multiplied with the density of the. Atomic mass the quantity of matter contained in an atom of an element. How its assessed.
The velocity of an electron v is equal to the group velocity v g of the associated wave. The compositions of various human tissues was taken from ICRU Report 44 1989. The conservation of mass is the fundamental concept of physics.
The unit of mass in the International System of Units SI is the kilogram which. It is expressed as a multiple of one-twelfth the mass of the carbon-12 atom 1992646547 1023 gram which is assigned an atomic mass of 12 units. It is in effect the resistance that a body of matter offers to a change in its speed or position upon the application of a force.
An objects center of mass is the point at which it can be balanced. Values are given for the mean ratio of atomic number-to-mass ZA the mean excitation energy I and the density ρ. In fact it has to be equal to the mass m 1 multiplied by the acceleration.
In this case the mass is accelerating to the right since it is moving in. Learn the definition of center of mass and learn how to calculate it. 1 hour 45 minutes.
Learn the definition of center of mass and learn how to calculate it. In physics and chemistry the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter and energy the mass of the system must remain constant over time as the systems mass cannot change so quantity can neither be added nor be removed. According to Newtons First Law of motion an object remains in the same state of motion unless a resultant force acts on it.
Material constants and composition assumed in the present evaluations for compounds and mixtures. Hence mass is neither created nor destroyed. In this scale 1 atomic mass unit amu corresponds to 1660539040 1024 gram.
The atomic mass unit is also called the dalton Da after English. The stiffness of each spring and the amount of. The mass of an electron in the periodic potentials of a crystal is different from the free electron mass and is usually referred to as the effective mass.
Sometimes the center of mass is directly in the center of an object. There are two springs having diferent spring constants and there are five different masses 1-kg 2-kg 3-kg 4-kg and an unknown mass that can be hung from the spring. It is the part of thermodynamics physics.
If the resultant force on an object is zero this means. The Mass on a Spring Interactive provides the user with a richly-interactive environment for investigating the periodic motion of a mass on a spring. According to de Broglie hypothesis a moving electron is associated with a wave.
If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website.

Mass Vs Weight The Difference Between Mass And Weight Physics Lessons Learning Science Physics And Mathematics

Difference Between Mass And Weight Physics Classroom Learn Physics Physics Notes
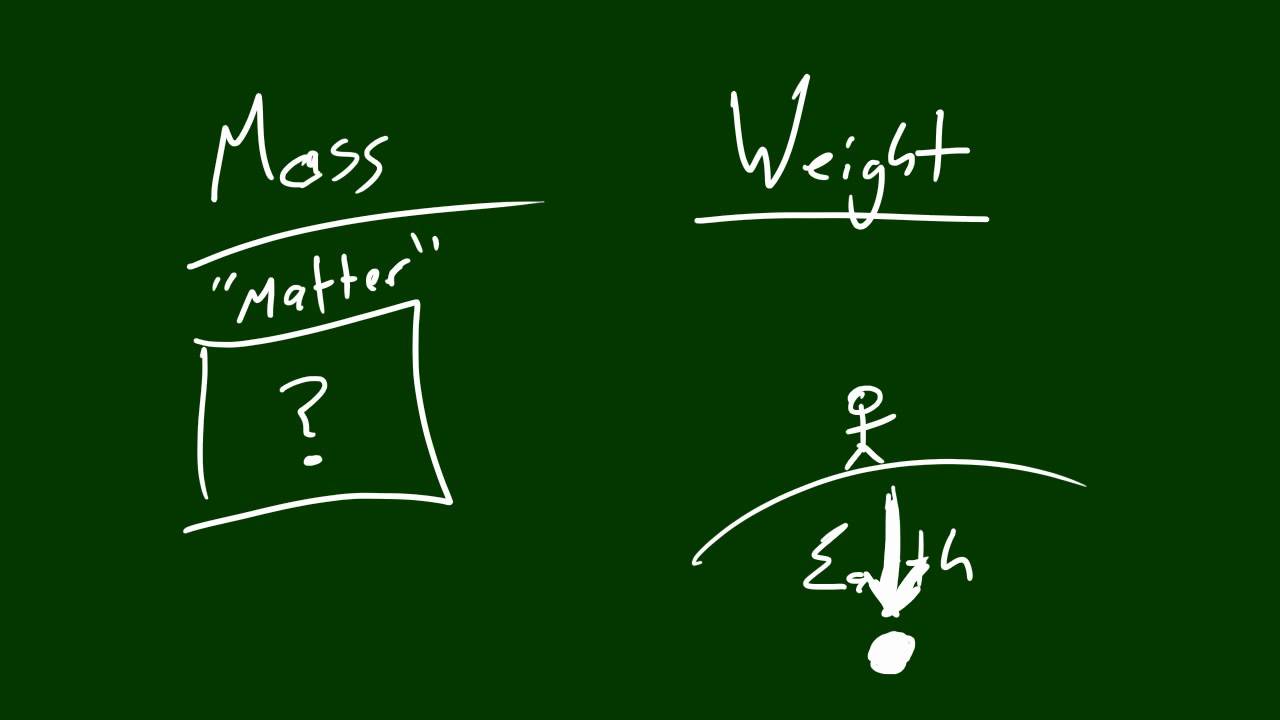
Physics Lecture 14 Mass Vs Weight Physics Lecture Physical Science

How To Calculate Mass 10 Steps With Pictures Wikihow Measuring Mass Mass Force Physics
Comments
Post a Comment